AI for Pipe Conveyor System
What is pipe conveyor?
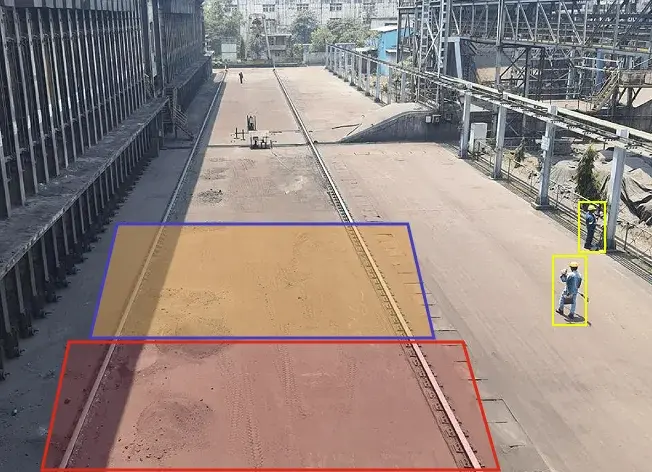
A Pipe Conveyor is a type of belt conveyor where the belt folds into a closed, circular tube while carrying material. The belt edges overlap to form this pipe shape, which keeps the material fully enclosed during transport. This enclosed design helps prevent spillage, reduces dust, and avoids contamination. Pipe conveyors are also useful because they can follow sharp curves, handle steep inclines, and fit into complex plant layouts where normal conveyors cannot. They can even run in both directions, making them more versatile.
Where pipe conveyor is mostly used?
Pipe conveyors are primarily used in industries that require enclosed, dust-free, and spill-free material transportation over long distances and complex routes. They are widely deployed in steel plant RMHS systems for handling iron ore, coal, fluxes, and sinter mix; in cement plants for transporting clinker, limestone, additives, and alternative fuels; and in power plants for clean and reliable movement of coal from stockyards to boilers. Additionally, they are essential in mining operations for conveying ores and aggregates across uneven terrain, and in ports and terminals for environmentally compliant handling of bulk materials such as coal, cement, and fertilizers.
What causes pipe conveyors break down?
- Improper Folding and Unfolding: Sticky or moist materials disrupt smooth flat-to-pipe and pipe-to-flat transitions, causing belt jamming, blockages, and unstable material flow.
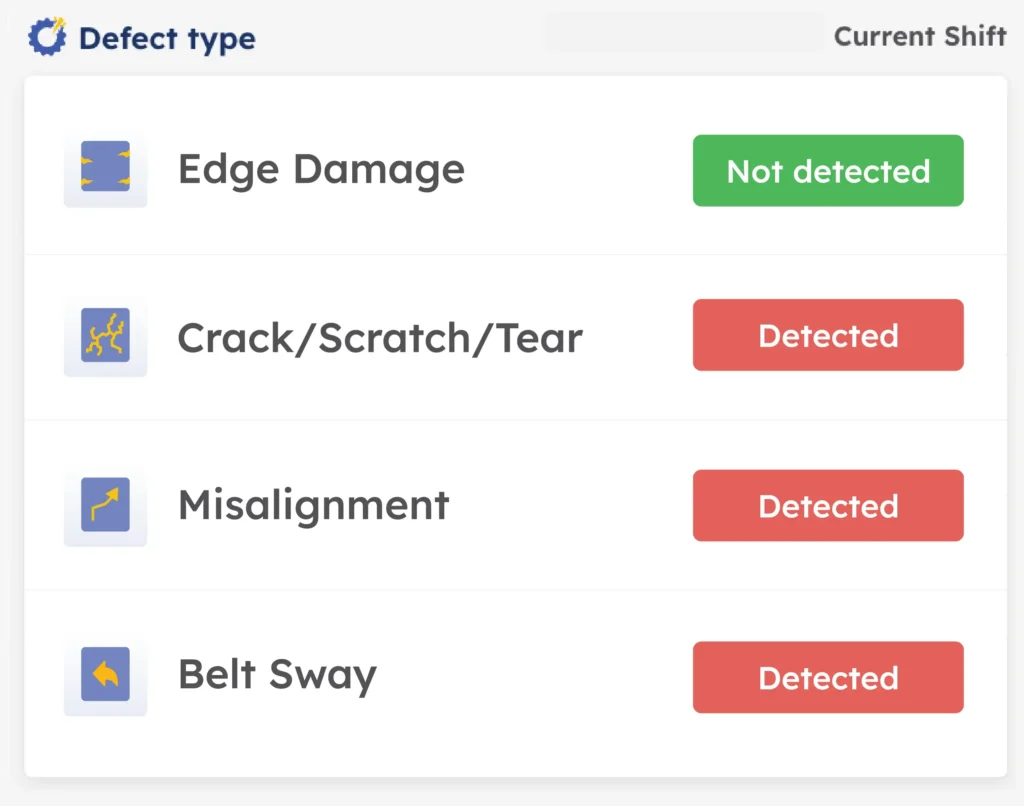
- Belt Sway, Misalignment & Tracking Issues: Excessive lateral movement, poor tracking, or overlap errors disturb pipe formation. Minor sway accelerates wear, while major sway risks partial pipe collapse and serious mechanical stress.
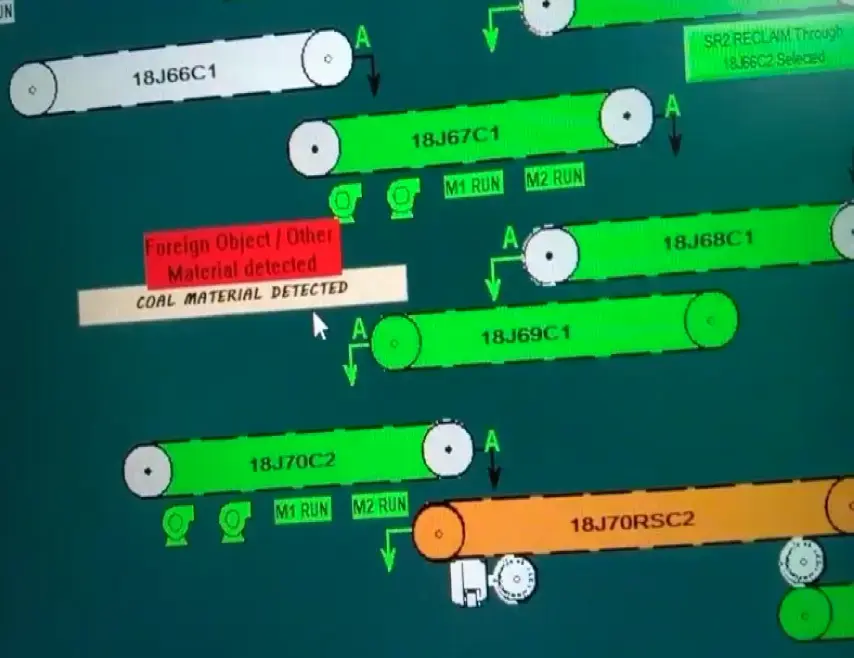
- Foreign Object Ingress: Wooden pieces, large rocks, and metal scraps interfere with pipe formation, damage the belt surface, and lead to abrupt stoppages.
- Material Build-Up & Surface Wear: Fine or sticky materials accumulate on the belt, affecting pipe shaping, increasing power consumption, and causing progressive wear that remains unnoticed without continuous monitoring.
- High Load on Rollers and Idlers: The torsional twist needed for pipe formation places heavy stress on rollers, idlers, and belt edges, accelerating component wear and increasing failure risk.
- Difficult Maintenance and Inspection: The enclosed structure limits visibility, making it harder to detect early signs of wear, misalignment, or damage without automated monitoring.
- Risk of Unplanned Downtime: Any unresolved issue—alignment, unfolding, obstruction, or component stress—rapidly escalates into conveyor stoppages and major operational disruptions.
Ripik AI platform for pipe conveyor monitoring
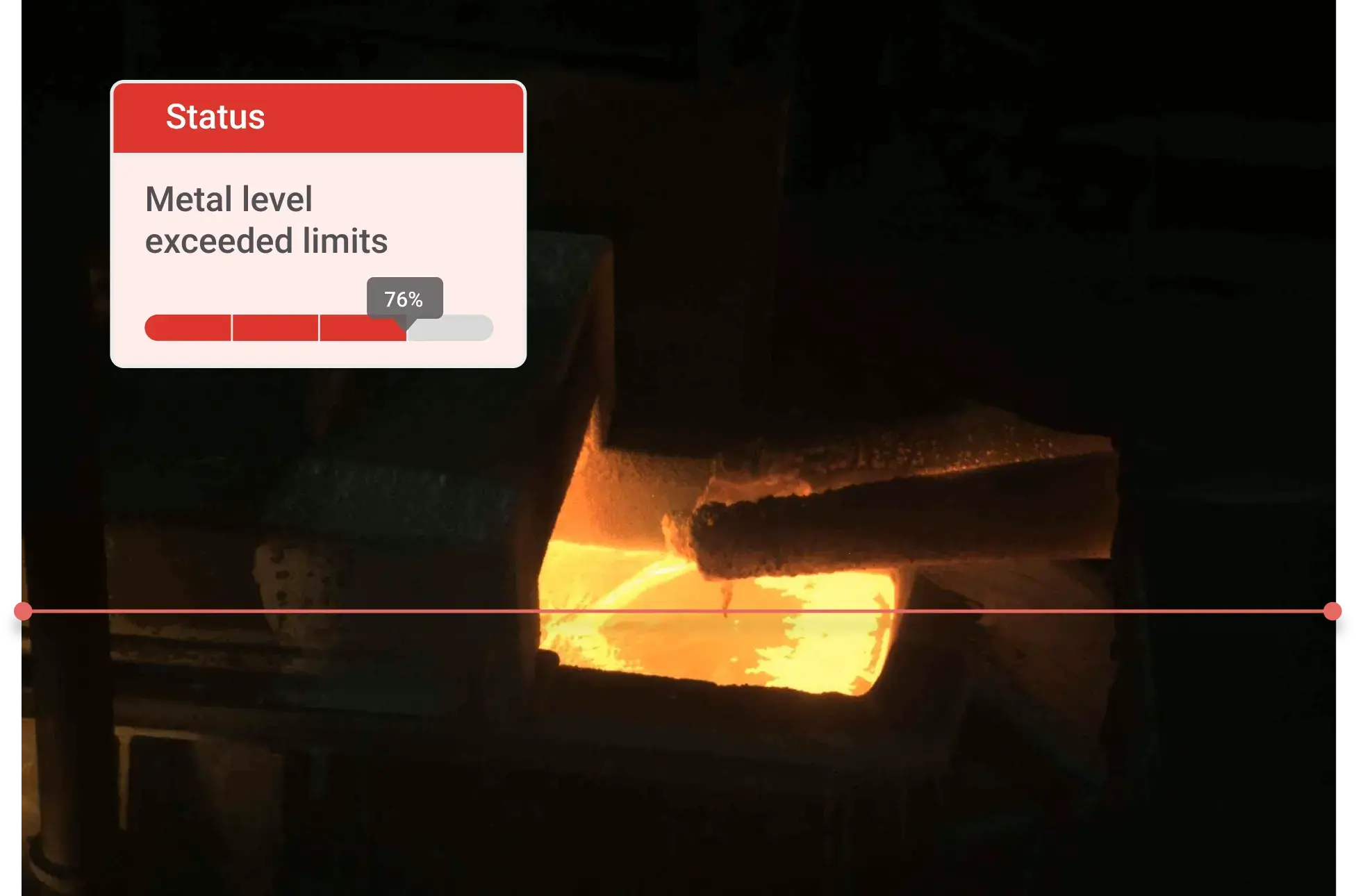
Ripik AI enables real-time monitoring of pipe conveyor belts, precisely identifying belt sway, improper folding and unfolding, foreign object entry, wear and tear, spillage, misalignment, and material build-up with exceptional accuracy. The system raises instant alerts through dashboards, WhatsApp, or email whenever anomalies are detected, and integrates with the PLC to automatically stop the conveyor belt during critical events. This ensures stable pipe formation, prevents breakdowns, minimizes downtime, and significantly enhances overall reliability and safety.
Key Features
Key Impact of Pipe Conveyor Monitoring
- Reduced Downtime: Early detection of belt sway, unfolding issues, and foreign objects prevents unexpected stoppages and production delays.
- Improved Safety: Real-time alerts and PLC-controlled emergency stops reduce operator risk and protect equipment from catastrophic failures.
- Extended Belt Life: Continuous monitoring of wear, misalignment, and material build-up minimizes mechanical stress and prolongs conveyor lifespan.
- Higher Operational Efficiency: Stable pipe formation and smooth material flow enhance throughput and reduce energy losses.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Predictive insights and historical data help schedule timely interventions, avoiding costly repairs and unplanned shutdowns.
- Enhanced Reliability: Constant visibility into belt behavior ensures consistent, safe, and uninterrupted operation across RMHS and bulk-handling environments.