Big Rock Detection
Prevent crusher breakdown in cement plant Introducing JamGuard- Prevent Crusher Jams and Eliminate Downtime...
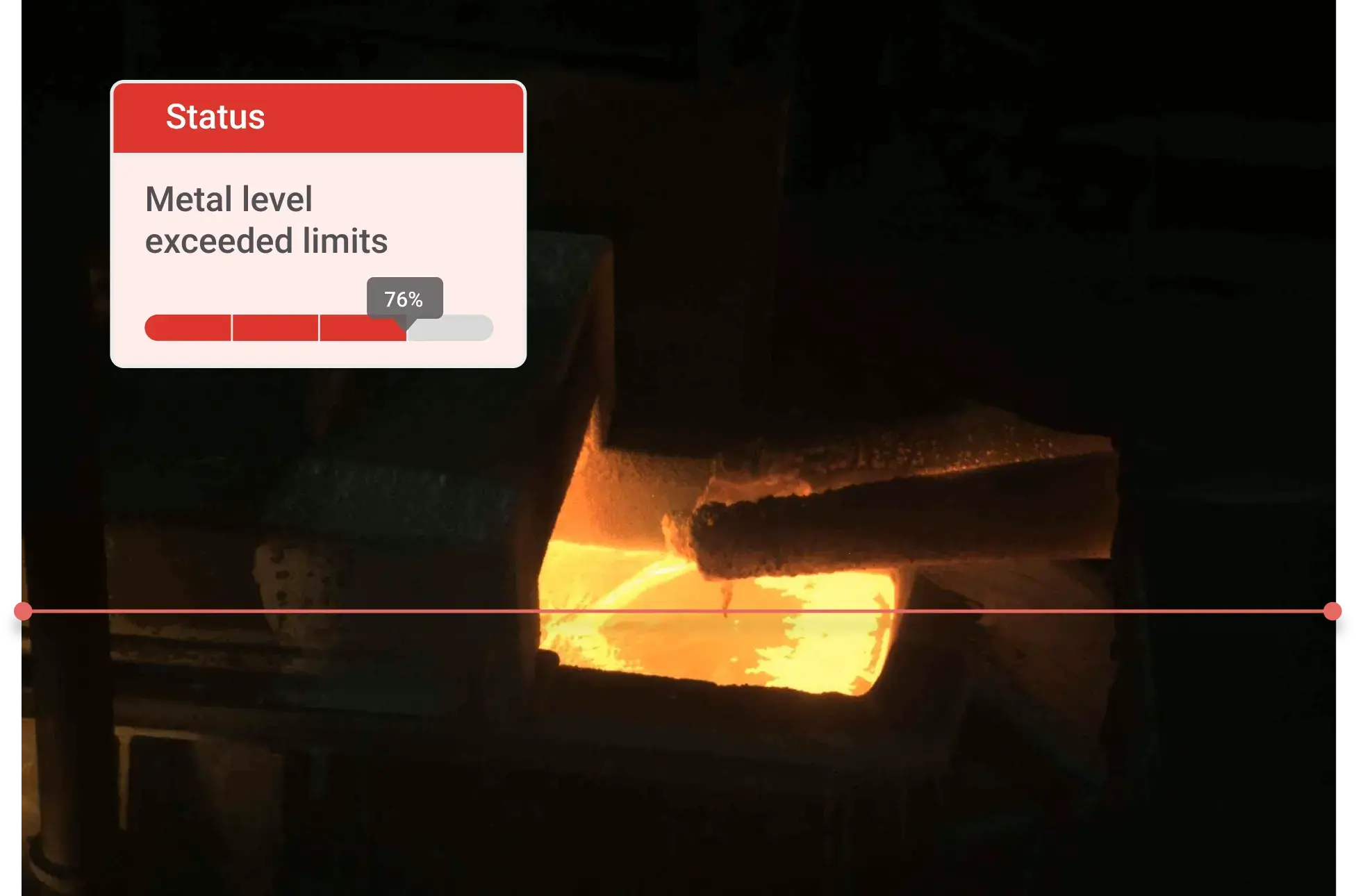
Ladle Management
Vision AI agents tracks ladle movements, reducing the risk of spills, accidents, and misalignment, causing...
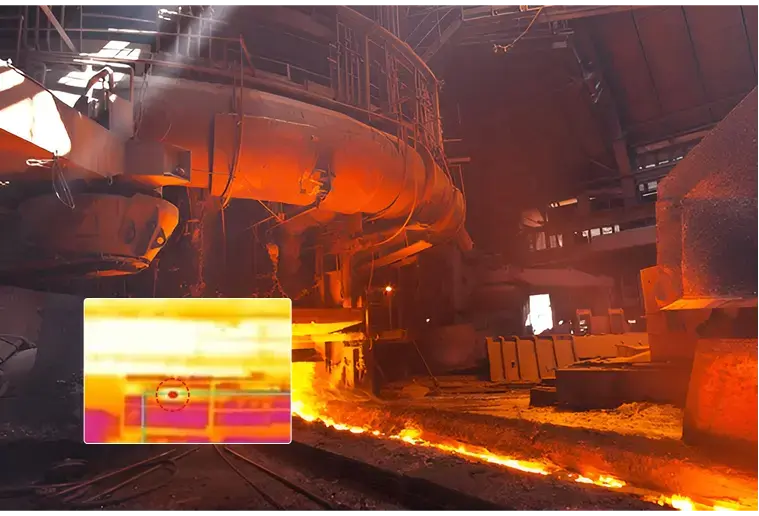
Blast Furnace Operations
Enhance blast furnace stability, efficiency, and productivity with AI agents driven insights.
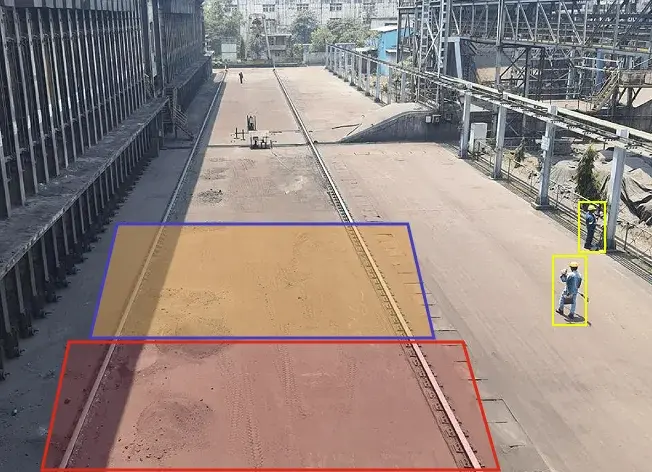
Stockpile Management
Gain real-time, accurate measurements to improve stockpile inventory management, reduce waste, and enhance...
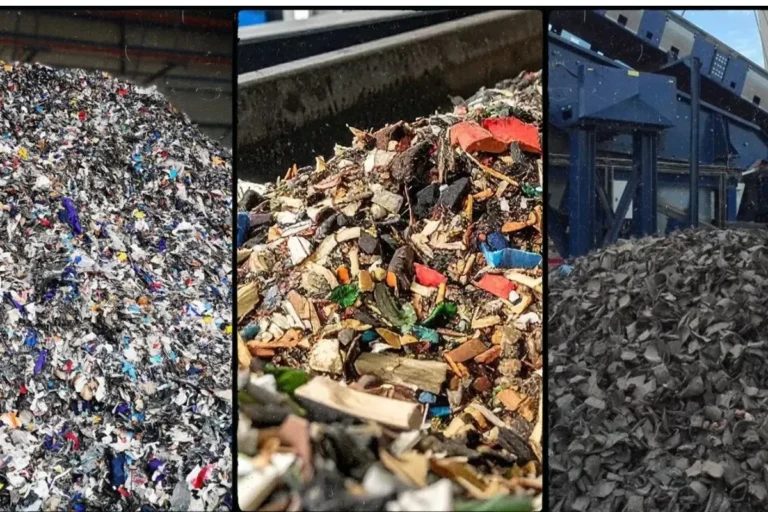
Alternative Fuels
AI for Calorific Value Estimation Optimize Alternative Fuels in cement industry with MatScan – our AI...
Moisture Detection
Enhance energy efficiency with real-time AI agents to manage material moisture analysis with IR Came...
Kiln Refractory Monitoring
Reduce unexpected downtime, gradual wear, and degradation of refractory linings in cement kilns
Cement kiln
Elevate cement kiln operations and achieve optimal process control every time with our AI agents.
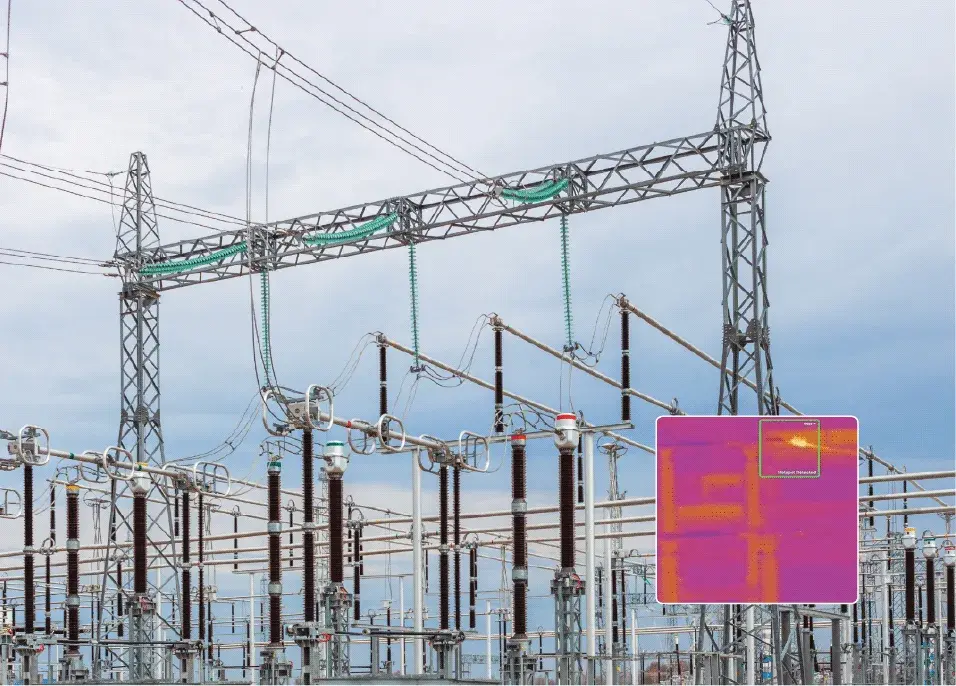
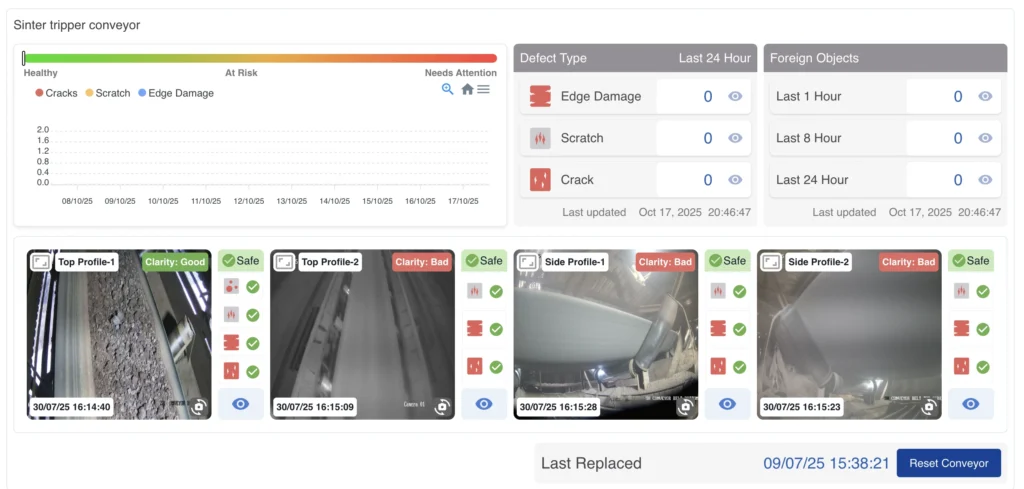
Conveyor Belt Monitoring
AI agents manage conveyor systems by providing real-time insights, detecting wear, misalignment, and...